DSR: Direct Self-rectification for Uncalibrated Dual-lens Cameras
Ruichao Xiao, Wenxiu Sun, Jiahao Pang, Qiong Yan, Jimmy Ren
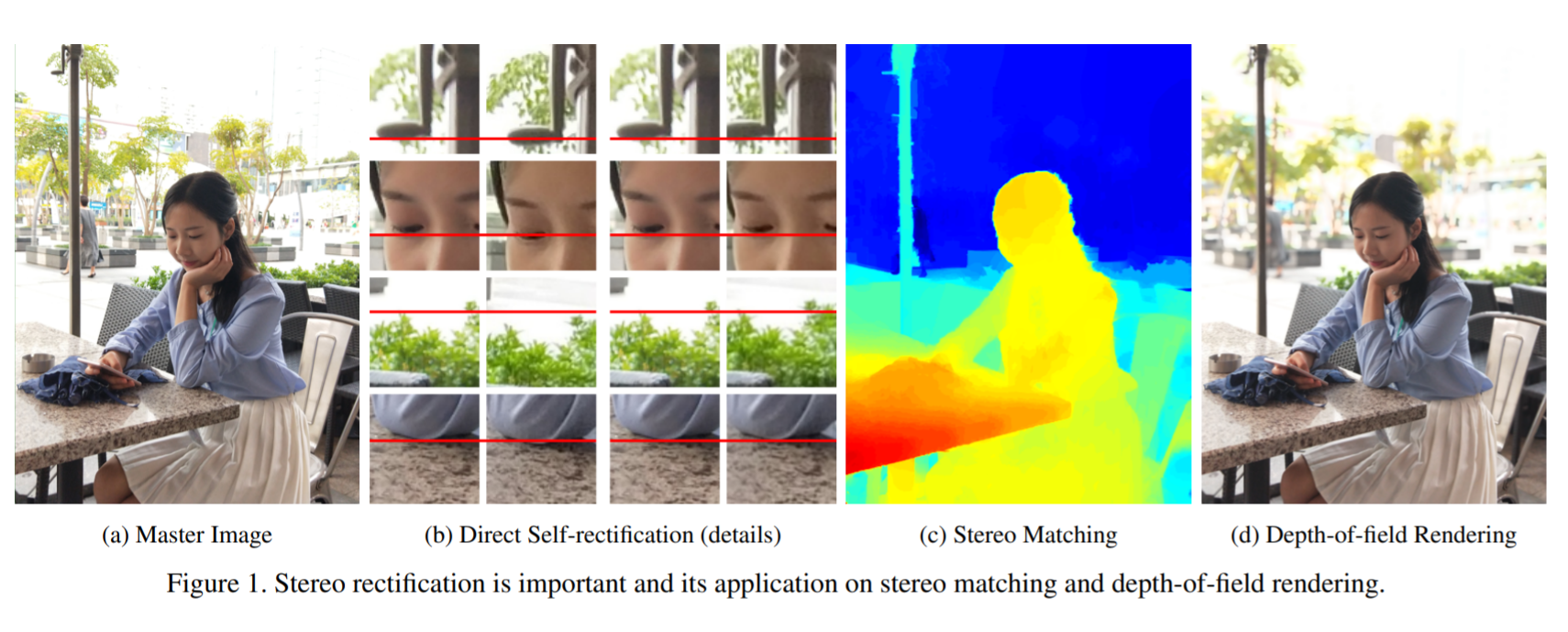
With the developments of dual-lens camera modules, depth information representing the third dimension of the captured scenes becomes available for smartphones. It is estimated by stereo matching algorithms, taking as input the two views captured by dual-lens cameras at slightly different viewpoints. Depth-of-field rendering (also be referred to as synthetic defocus or bokeh) is one of the trending depth-based applications. However, to achieve fast depth estimation on smartphones, the stereo pairs need to be rectified in the first place. In this paper, we propose a cost-effective solution to perform stereo rectification for dual-lens cameras called direct self-rectification, short for DSR 1 . It removes the need of individual offline calibration for every pair of dual-lens cameras. In addition, the proposed solution is robust to the slight movements, e.g., due to collisions, of the dual-lens cameras after fabrication. Different with existing self-rectification approaches, our approach computes the homography in a novel way with zero geometric distortions introduced to the master image. It is achieved by directly minimizing the vertical displacements of corresponding points between the original master image and the transformed slave image. Our method is evaluated on both realistic and synthetic stereo image pairs, and produces superior results compared to the calibrated rectification or other self-rectification approaches.